Injury Information
Hip Bursitis
What is Hip Bursitis?
Hip bursitis is the inflammation of one or more of the bursae (small, fluid-filled sacs) located near the hip joint. The bursae act as cushions to reduce friction and provide smooth movement between bones and soft tissues, such as muscles and tendons. In hip bursitis, the bursae become inflamed, typically due to repetitive motion or prolonged pressure, leading to pain and discomfort in the hip area. It is most commonly seen in the trochanteric bursa on the outside of the hip.
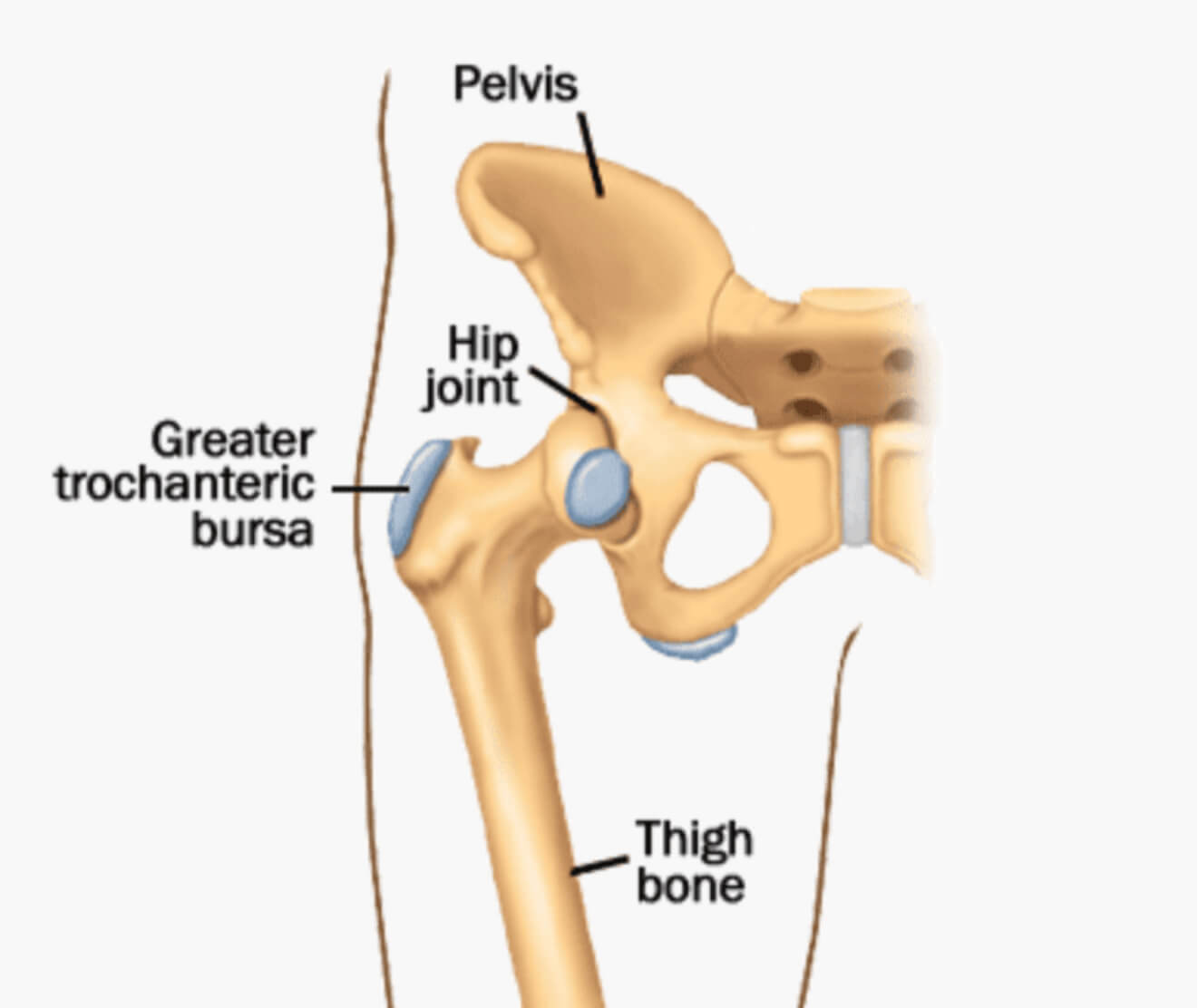
Types of Hip Bursitis
Hip bursitis is classified as an inflammatory condition. There are two main types of hip bursitis:
- Trochanteric Bursitis: The most common form, affecting the bursa on the outer side of the hip (greater trochanter).
- Ischial Bursitis: This affects the bursa located at the base of the buttocks, near the ischial tuberosity (sit bones).
It is often caused by repetitive motions, direct trauma, or overuse, especially in athletes, manual laborers, or those with certain postural issues.
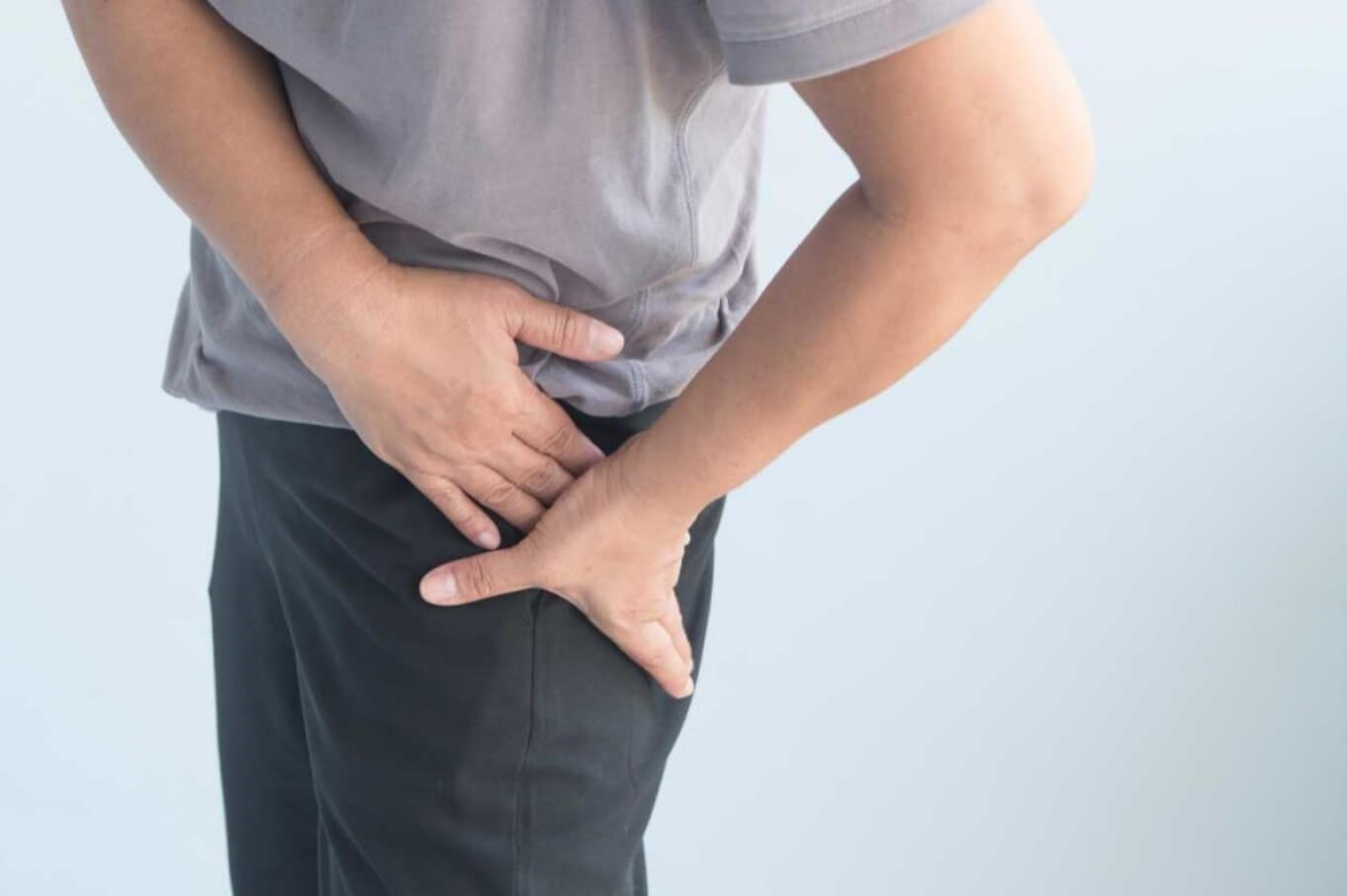
What Are the Symptoms of Hip Bursitis?
The main symptoms of hip bursitis include
- Pain on the outer side of the hip, which may worsen with movement or pressure
- Tenderness over the hip joint, particularly on the outer thigh near the greater trochanter
- Pain when lying on the affected side, making sleep difficult
- Stiffness and limited range of motion in the hip
- Pain during activities like walking, climbing stairs, or rising from a seated position
- Swelling around the hip joint (in some cases)
The pain is often described as sharp or aching, and it may radiate down the outside of the thigh.

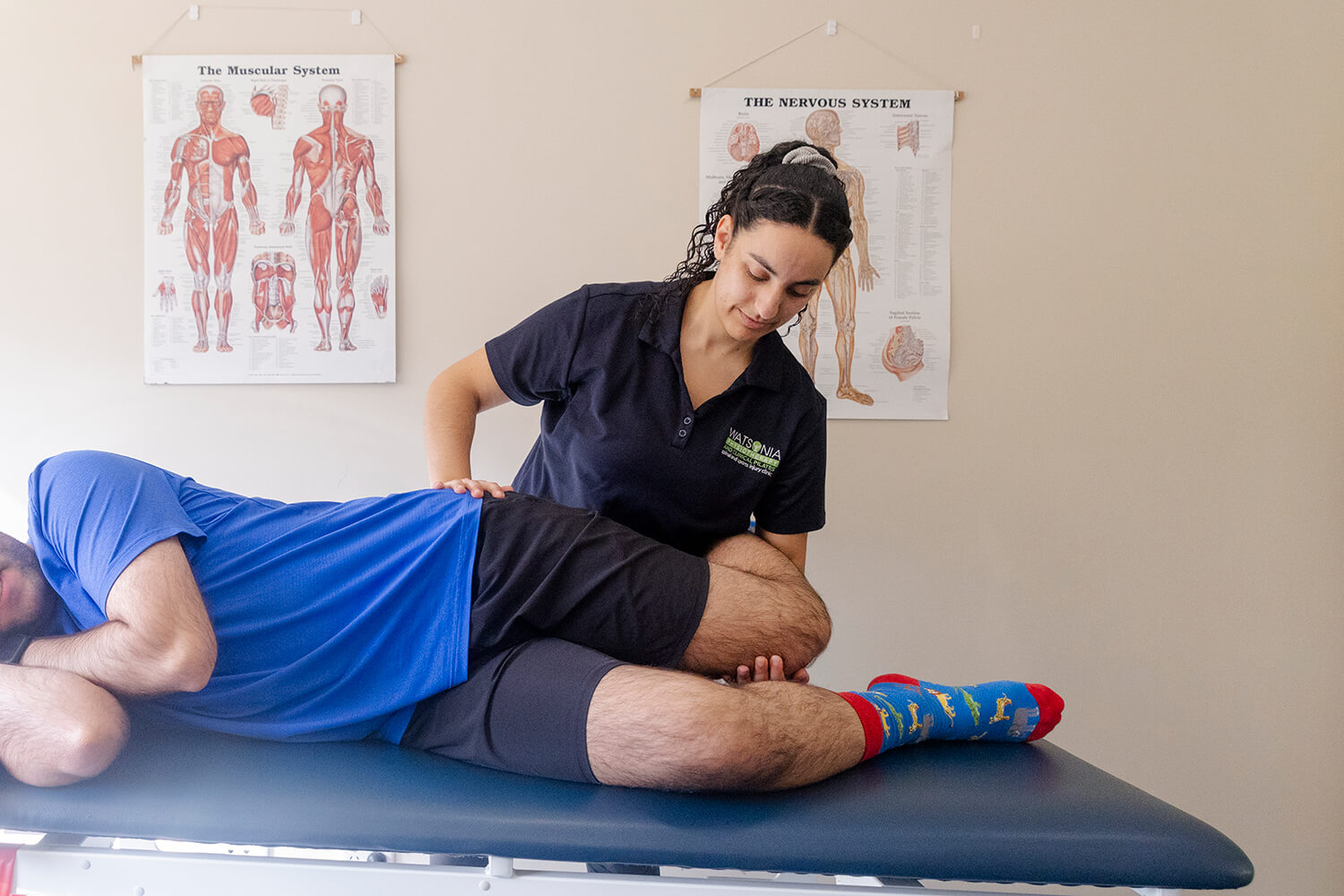
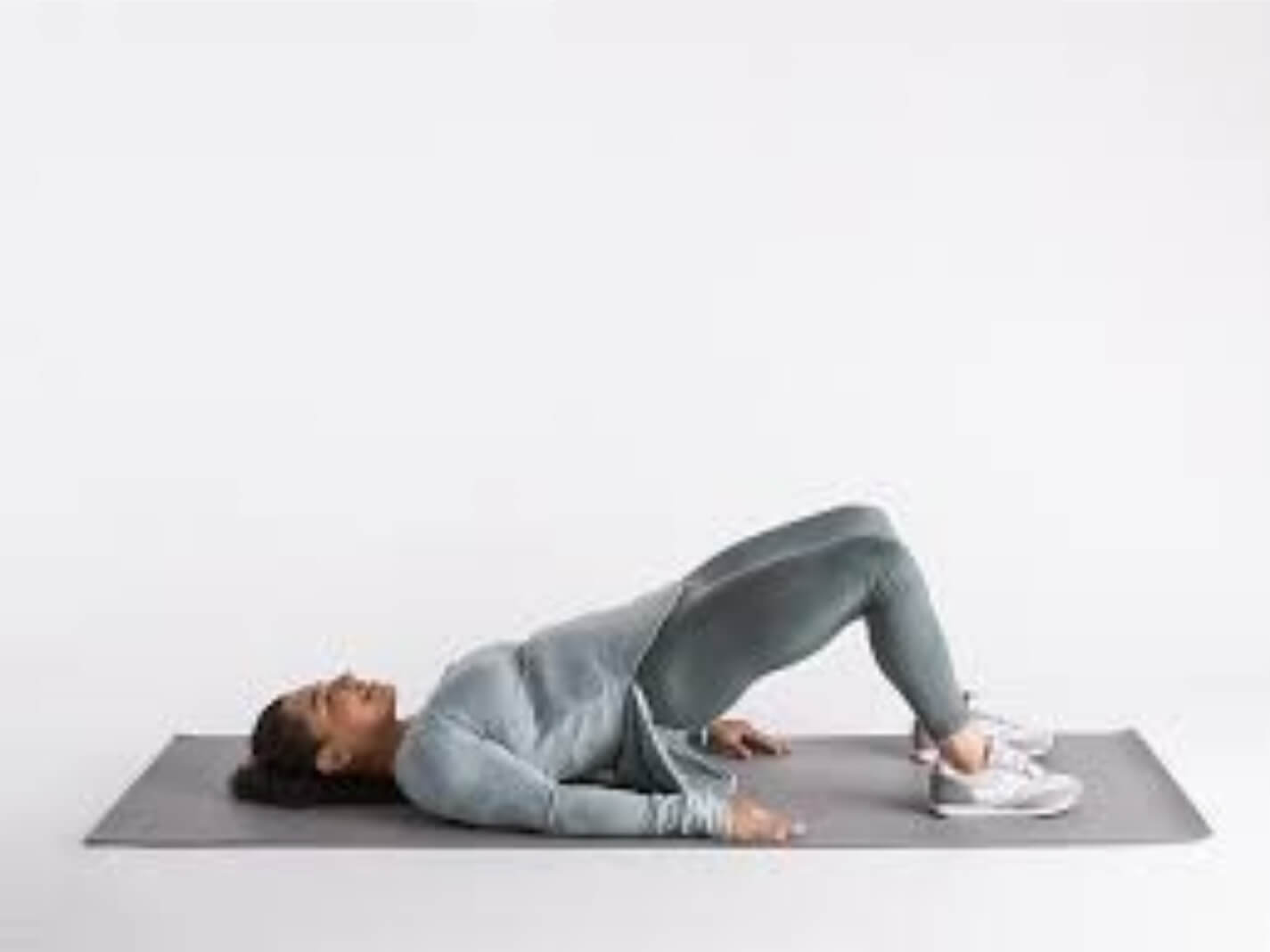
How Can Physiotherapy Help?
Physiotherapy plays a key role in treating hip bursitis and preventing future recurrences. A physiotherapist may use various techniques to help manage the condition:
- Load management: Monitoring and adjusting the amount of activity you do can help optimise muscle loading.
Manual therapy: Soft tissue mobilizations, joint mobilizations, or massage can help reduce pain, improve movement, and relax tight muscles around the hip. - Stretching exercises: Targeted stretches for the hip muscles, including the IT band, hip flexors, and glutes, can help improve flexibility and reduce strain on the bursae.
- Strengthening exercises: Strengthening weak muscles around the hip (such as the hip abductors and glutes) helps support the joint and reduce pressure on the bursa.
- Posture and body mechanics education: A physiotherapist can teach you how to avoid positions and movements that might irritate the bursa, as well as provide guidance on safe lifting and walking techniques.
- Recommendations for cortisone injections: In discussion with your doctor, a cortisone injection may be recommended to help reduce inflammation and relieve pain if other techniques are not working.
What Can You Do At Home?
There are several strategies to manage hip bursitis symptoms at home
- Rest: Avoid activities that trigger pain or put strain on the hip joint, such as prolonged standing or heavy lifting.
- Ice: Apply an ice pack to the hip for 15-20 minutes at a time, several times a day, to reduce inflammation and pain.
- Over-the-counter pain relief: NSAIDs like ibuprofen or naproxen can help reduce inflammation and provide pain relief.
- Gentle stretches and strengthening: Once the pain starts to subside, gentle stretching and strengthening exercises for the hip can help restore mobility and prevent future flare-ups.
- Positioning: When sleeping, try lying on the unaffected side or using pillows to cushion the affected hip for better comfort.

Cortisone Injections: What You Should Know
In cases where conservative treatments like rest and physiotherapy don’t provide sufficient relief, a cortisone injection may be recommended. Here’s what to know about it:
- What is it? A cortisone injection is a corticosteroid medication injected directly into the bursa to reduce inflammation and alleviate pain.
- When is it used? Cortisone injections are typically used when pain and inflammation persist, even after rest and physiotherapy. They can be very effective for providing quick relief.
- How does it work? The steroid helps reduce inflammation in the bursa, providing significant pain relief. The effects can last anywhere from a few weeks to several months.
- Risks and Considerations: While cortisone injections can be very effective, they are not a cure for bursitis. Repeated injections should be avoided, as they can weaken the tissues and tendons around the joint. Your healthcare provider will generally limit the number of injections.
- What to expect: After the injection, you may experience a temporary increase in pain before feeling the benefits, which usually take a few days to a week to fully manifest.
Recovery Time
The recovery time for hip bursitis depends on the severity of the inflammation and the treatment approach. Generally:
- Mild cases may recover within a few weeks with proper rest, ice therapy, and physiotherapy.
- Moderate to severe cases may take 6-12 weeks for full recovery.
- Cortisone injections can provide relief, but it’s still important to follow up with physiotherapy and a gradual return to activity to prevent re-injury.
With the right treatment plan, most people can fully recover from hip bursitis and return to their normal activities.

